 简单实现web服务器
简单实现web服务器
# 实现简单的web服务器
既然需要手动实现一个web服务器,那么先要了解什么是web服务器?
web服务器:严格意义上Web服务器只负责处理HTTP协议,只能发送静态页面的内容。而JSP,ASP,PHP等动态内容需要通过CGI、FastCGI、ISAPI等接口交给其他程序去处理。这个其他程序就是应用服务器。比如Web服务器包括Nginx,Apache,IIS等。而应用服务器包括WebLogic,JBoss等。应用服务器一般也支持HTTP协议,因此界限没这么清晰。但是应用服务器的HTTP协议部分仅仅是支持,一般不会做特别优化,所以很少有见Tomcat直接暴露给外面,而是和Nginx、Apache等配合,只让Tomcat处理JSP和Servlet部分
现在我们知道了,web服务器只实现,处理http协议,发送静态页面。
# 超文本传输协议(HTTP)
HTTP 是一种协议,允许 web 服务器和浏览器通过互联网进行来发送和接受数据。它是一种请求和响应协议。客户端请求一个文件而服务器响应请求。HTTP 使用可靠的 TCP 连接--TCP 默认使用 80 端口。第一个 HTTP 版是 HTTP/0.9,然后被 HTTP/1.0 所替代。
# http请求
# http响应
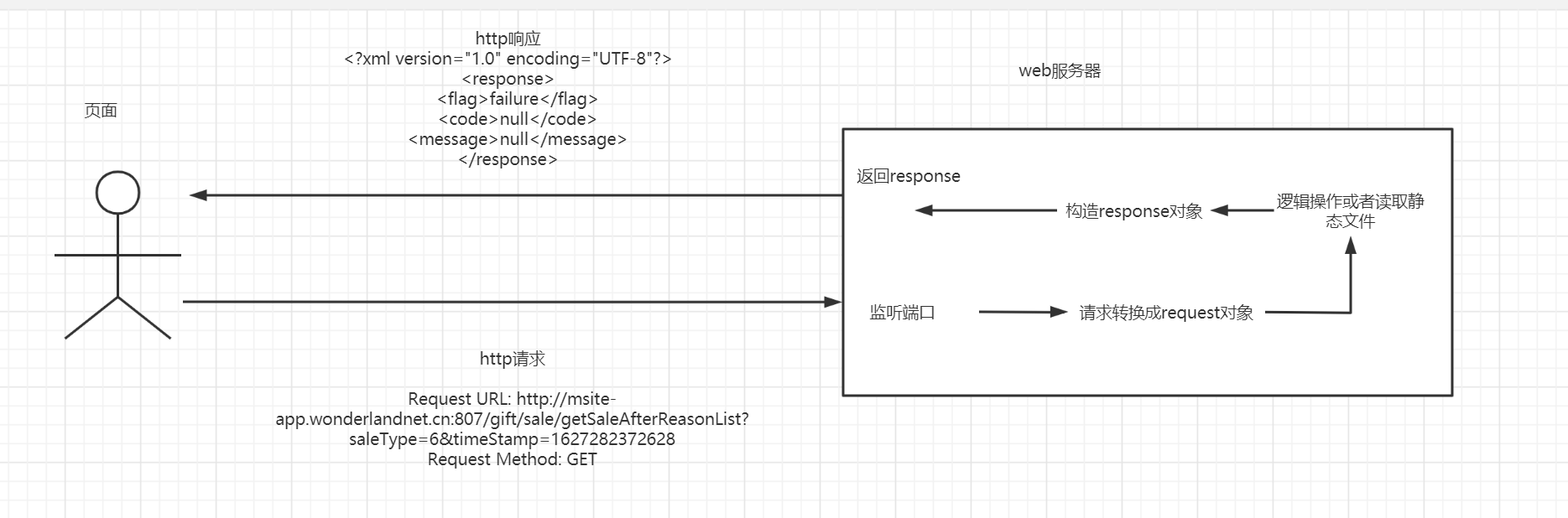
这里主要的流程,如何将监听端口,请求转换成request对象,响应如何转换成reponse,这里就要介绍socket
# socket(套接字)
常用的几个方法
// 与地址和端口绑定
Socket(InetAddress address, int port)
/**
* 与客户端连接
* Connects this socket to the server.
*
* @param endpoint the {@code SocketAddress}
* @throws IOException if an error occurs during the connection
* @throws java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException
* if this socket has an associated channel,
* and the channel is in non-blocking mode
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if endpoint is null or is a
* SocketAddress subclass not supported by this socket
* @since 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
public void connect(SocketAddress endpoint) throws IOException {
connect(endpoint, 0);
}
/**
* 返回此套接字的输入流。
如果此套接字具有关联的通道,则生成的输入流将其所有操作委托给该通道。 如果通道处于非阻塞模式,则输入流的read操作将抛出java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException 。
在异常情况下,底层连接可能被远程主机或网络软件破坏(例如在 TCP 连接的情况下重置连接)。 当网络软件检测到断开的连接时,以下内容适用于返回的输入流:-
网络软件可能会丢弃由套接字缓冲的字节。 可以使用read未被网络软件丢弃的字节。
如果套接字上没有缓冲的字节,或者所有缓冲的字节都已被read消耗,则对read所有后续调用都将抛出IOException 。
如果套接字上没有缓冲字节,并且没有使用close关闭套接字,则available将返回0 。
关闭返回的InputStream将关闭关联的套接字。
返回:
用于从此套接字读取字节的输入流。
抛出:
IOException – 如果在创建输入流时发生 I/O 错误、套接字关闭、套接字未连接或使用shutdownInput()关闭套接字输入
*/
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
if (isClosed())
throw new SocketException("Socket is closed");
if (!isConnected())
throw new SocketException("Socket is not connected");
if (isInputShutdown())
throw new SocketException("Socket input is shutdown");
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<>() {
public InputStream run() throws IOException {
return impl.getInputStream();
}
});
} catch (java.security.PrivilegedActionException e) {
throw (IOException) e.getException();
}
return is;
}
/**
*返回此套接字的输出流。
如果此套接字具有关联的通道,则生成的输出流将其所有操作委托给该通道。 如果通道处于非阻塞模式,则输出流的write操作将抛出java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException 。
关闭返回的OutputStream将关闭关联的套接字。
返回:
用于将字节写入此套接字的输出流。
抛出:
IOException – 如果在创建输出流时发生 I/O 错误或套接字未连接。
*/
public OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException {
if (isClosed())
throw new SocketException("Socket is closed");
if (!isConnected())
throw new SocketException("Socket is not connected");
if (isOutputShutdown())
throw new SocketException("Socket output is shutdown");
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<>() {
public OutputStream run() throws IOException {
return impl.getOutputStream();
}
});
} catch (java.security.PrivilegedActionException e) {
throw (IOException) e.getException();
}
return os;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
Socket提出了他的规范,而要实现客户端与服务端的通信,需要使用他的实现类java.net.ServerSocket 类
接下来,要实现一个简单的web服务器,就是靠httpServer啦。它既负责接受请求,解析请求,也负责将请求的资源响应给浏览器。
public class HttpServer {
/**
* WEB_ROOT is the directory where our HTML and other files reside.
* For this package, WEB_ROOT is the "webroot" directory under the working
* directory.
* The working directory is the location in the file system
* from where the java command was invoked.
*/
public static final String WEB_ROOT = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + "webroot";
// shutdown command
private static final String SHUTDOWN_COMMAND = "/SHUTDOWN";
// the shutdown command received
private boolean shutdown = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpServer server = new HttpServer();
// 调用接受请求的方法
server.await();
}
public void await() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
int port = 8080;
try {
// 创建一个serverSocket实例
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// Loop waiting for a request
while (!shutdown) {
Socket socket = null;
InputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
try {
socket = serverSocket.accept();
input = socket.getInputStream();
output = socket.getOutputStream();
// create Request object and parse
Request request = new Request(input);
request.parse();
// create Response object
Response response = new Response(output);
response.setRequest(request);
// 发静态资源
response.sendStaticResource();
// Close the socket
socket.close();
//check if the previous URI is a shutdown command
shutdown = request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
我们可以看到,程序启动后,会进入到wait()方法,开始创建serverSocket实例,进入到while里面的accept方法,而accept是阻塞的,只有请求进来时,才会执行,否则会一直阻塞在这。
当一个请求进来时,可以从套接字拿出输入,输出流,输入流可以拿到请求的url,port,headers一些信息,输出流就是帮助我们写入一些东西,然后再将写入的东西响应出去啦。Request request = new Request(input); 这里的request是一个简易版的,主要作用是帮助更好的获取信息,输入流传入进去,会解析uri,那样就不需要自己手动解析uri啦;Response response = new Response(output); 而response 提供了一个发送静态资源的方法,根据WEB_ROOT 提供的路径来查找要返回的资源。
如果浏览器上请求这样的地址127.0.0.1:8080/shutdown ,shutdown = request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND); 这句话就会起作用了,使while循环失效,主方法结束,程序结束。
效果图
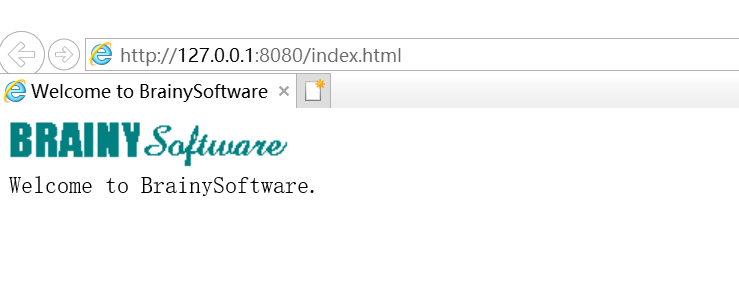
下面附上request,response的代码
# request
public class Request {
private InputStream input;
private String uri;
public Request(InputStream input) {
this.input = input;
}
public void parse() {
// Read a set of characters from the socket
StringBuffer request = new StringBuffer(2048);
int i;
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
try {
i = input.read(buffer);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
i = -1;
}
for (int j=0; j<i; j++) {
request.append((char) buffer[j]);
}
System.out.print(request.toString());
uri = parseUri(request.toString());
}
private String parseUri(String requestString) {
int index1, index2;
index1 = requestString.indexOf(' ');
if (index1 != -1) {
index2 = requestString.indexOf(' ', index1 + 1);
if (index2 > index1)
return requestString.substring(index1 + 1, index2);
}
return null;
}
public String getUri() {
return uri;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# response
public class Response {
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
Request request;
OutputStream output;
public Response(OutputStream output) {
this.output = output;
}
public void setRequest(Request request) {
this.request = request;
}
public void sendStaticResource() throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
File file = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT, request.getUri());
if (file.exists()) {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
while (ch!=-1) {
output.write(bytes, 0, ch);
ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
}
}
else {
// file not found
String errorMessage = "HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html\r\n" +
"Content-Length: 23\r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"<h1>File Not Found</h1>";
output.write(errorMessage.getBytes());
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
// thrown if cannot instantiate a File object
System.out.println(e.toString() );
}
finally {
if (fis!=null)
fis.close();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
源码地址https://gitee.com/zxqzhuzhu/tomcat-how-to-work-original
如果有需要可以关注公众号,领取 how tomcat works中文版
