建立servlet容器
建立servlet容器
上一节实现简单的web容器,我们已经实现了一个简单的web服务器,客户端可以请求服务器上的静态文件,然后响应给客户端。
现在,我们需要再加一个功能,就是去请求一个操作,借助逻辑操作,帮我们完成一些事情,这时候就要使用servlet啦
# 什么是servlet
官方解释:
Servlet是sun公司提供的一门用于开发动态web资源的技术。 Sun公司在其API中提供了一个servlet接口,用户若想用发一个动态web资源(即开发一个Java程序向浏览器输出数据),需要完成以下2个步骤: 1、编写一个Java类,实现servlet接口。 2、把开发好的Java类部署到web服务器中。 按照一种约定俗成的称呼习惯,通常我们也把实现了servlet接口的java程序,称之为Servlet
按照我的理解:servlet是一种规范,只是规定了每种方法,tomcat会将解析好的request和response对象传入对应的servlet,供service() 写业务代码使用,
tomcat会根据客户端请求的url,去寻找你要请求的servlet,然后调用service()方法,从而达到实现业务逻辑。
public interface Servlet {
void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException;
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
String getServletInfo();
void destroy();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
下面开始手动实现servlet容器
文件结构
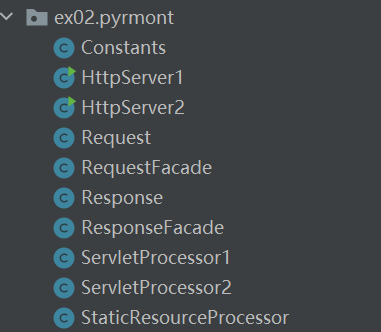
httpServer 主要用来监听客户端的请求,解析socket中的输入流和输出流给request和response对象,然后将request和response传入processor(处理器)
request:主要是将socket的输入流解析成一个request对象,里面提供一些请求信息,比如具有getUri()获取请求uri作用。
response: 主要是将socket的输入流解析成一个response对象,借助输出流将数据写入进去。
processor:主要是根据请求的uri路径,利用类加载器去实例化servlet对象,调用serive()方法
facade:
# httpServer1
public class HttpServer1 {
/** WEB_ROOT is the directory where our HTML and other files reside.
* For this package, WEB_ROOT is the "webroot" directory under the working
* directory.
* The working directory is the location in the file system
* from where the java command was invoked.
*/
// shutdown command
private static final String SHUTDOWN_COMMAND = "/SHUTDOWN";
// the shutdown command received
private boolean shutdown = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpServer1 server = new HttpServer1();
server.await();
}
public void await() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
int port = 8080;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// Loop waiting for a request
while (!shutdown) {
Socket socket = null;
InputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
try {
socket = serverSocket.accept();
input = socket.getInputStream();
output = socket.getOutputStream();
// create Request object and parse
Request request = new Request(input);
request.parse();
// create Response object
Response response = new Response(output);
response.setRequest(request);
// check if this is a request for a servlet or a static resource
// a request for a servlet begins with "/servlet/",如果uri的路径以/servlet开头,会进入到里面
if (request.getUri().startsWith("/servlet/")) {
// new一个servlet处理器,去加载servlet
ServletProcessor1 processor = new ServletProcessor1();
processor.process(request, response);
}
else {
// 创建静态资源处理器,加载静态资源
StaticResourceProcessor processor = new StaticResourceProcessor();
processor.process(request, response);
}
// Close the socket
socket.close();
//check if the previous URI is a shutdown command
shutdown = request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
首先,main方法执行,创建httpServer1对象,调用wait()方法。
其次,创建ServerSocket对象,监听服务器端的8080端口,然后进入while循环,调用accept()方法,如果没有请求进来,那么方法会一直被阻塞在这。
接下来,如果有一个请求进来了,解析输入流为request对象,输出流为response对象,然后根据request获取请求的uri。
如果以/servlet开头,那就实例化servletProcess,让他来处理servlet的逻辑操作,如果不是则实例化StaticResourceProcessor,去处理静态资源(这里就使用了java的多态特性,将共有的特性抽象出来,实际处理时根据子类的实现方式去实现)
最后,关闭socket.
大概流程就是这样,接下来我们具体关注process方法到底怎么实现的
ServletProcessor1:
public class ServletProcessor1 {
public void process(Request request, Response response) {
String uri = request.getUri();
String servletName = uri.substring(uri.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
URLClassLoader loader = null;
try {
// create a URLClassLoader
URL[] urls = new URL[1];
URLStreamHandler streamHandler = null;
File classPath = new File(Constants.WEB_ROOT);
// the forming of repository is taken from the createClassLoader method in
// org.apache.catalina.startup.ClassLoaderFactory
String repository = (new URL("file", null, classPath.getCanonicalPath() + File.separator)).toString() ;
// the code for forming the URL is taken from the addRepository method in
// org.apache.catalina.loader.StandardClassLoader class.
urls[0] = new URL(null, repository, streamHandler);
loader = new URLClassLoader(urls);
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString() );
}
Class myClass = null;
try {
myClass = loader.loadClass(servletName);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
Servlet servlet = null;
try {
servlet = (Servlet) myClass.newInstance();
servlet.service((ServletRequest) request, (ServletResponse) response);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
首先,我们可以从request拿到客户端请求的uri,利用URL对象构造出资源定位符对象,这个对象就封装了文件资源在服务器的位置(事先在webRoot下面放了一个Servlet文件)。
其次,再利用URLClassLoader去加载我们要执行的servlet
接下来,就是强转被加载出来的对象为servlet类型,执行serive()方法
是不是很简单!!
webRoot目录结构
PrimitiveServlet:
public class PrimitiveServlet implements Servlet {
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("init");
}
public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("from service");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("Hello. Roses are red.");
out.print("Violets are blue.");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
public String getServletInfo() {
return null;
}
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
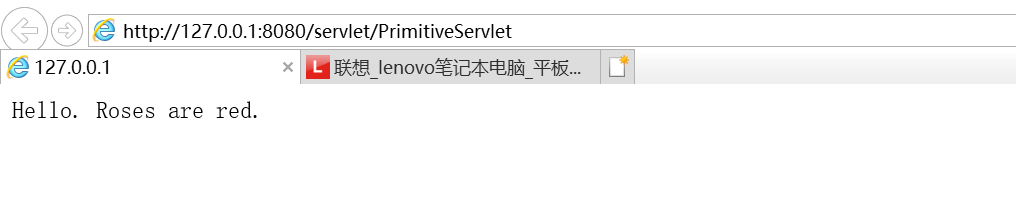
测试结果
浏览器请求结果
控制台打印结果

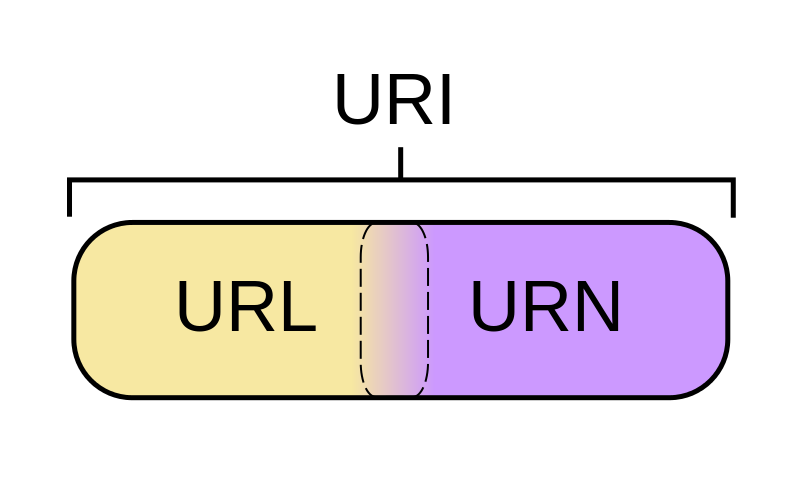
# url和uri的区别
URI = Universal Resource Identifier 统一资源标志符,用来标识抽象或物理资源的一个紧凑字符串。 URL = Universal Resource Locator 统一资源定位符,一种定位资源的主要访问机制的字符串,一个标准的URL必须包括:protocol、host、port、path、parameter、anchor。 URN = Universal Resource Name 统一资源名称,通过特定命名空间中的唯一名称或ID来标识资源。